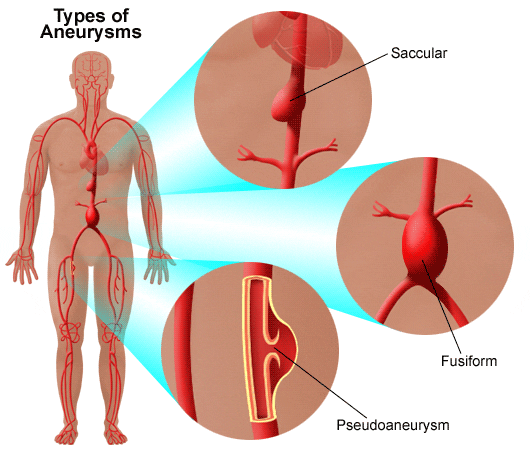
An aneurysm occurs when there is a weakening in one of the walls of the blood vessel causing it to dilate to one and a half times the normal diameter which typically is around 3 centimeters.
Once diagnosed, patients are followed by a vascular surgeon for the remainder of their lives. Things that warrant surgical repair include rapidly growing aneurysm, diameter greater than 5 cm or a symptomatic aneurysm (pain with palpation of the aneurysm).
Two surgical options for repair include endovascular repair with endograft placement or the traditional open repair. Endovascular is the preferred method of repair as there are less risks and most patients are discharged the following day. Open surgery is warranted for those that are not good candidates for endovascular repair. Those patients typically have anatomy not suitable for endograft placement. The open repair typically involves a large incision over the abdomen and approximately a one week hospitalization. CVT surgery is the preferred surgical group in the area for both of these procedures.